Gum boils are periodontal abscesses that develop on the gums. According to a review published in the IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences, the periodontal abscess is the third most common dental emergency and includes 6-14% of all dental emergencies. The abscess is filled with bacteria, and there is a danger that it can spread to other parts of the body. So, treating gumboils in urgency is required to avoid complications. Continue reading to learn about the symptoms, causes and treatments.
What Is a Gum Boil?
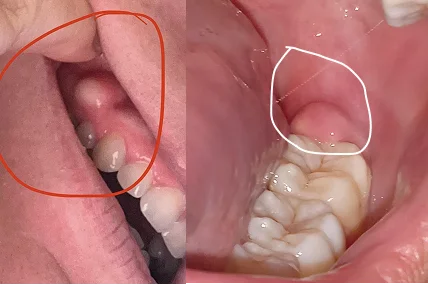
Gum boils are a type of periodontal abscess that appears red or white and feels soft and painful to the touch. They occur when bacteria invade the space between the tooth and gum, which ultimately results in poor oral hygiene and untreated gum disease.
In simple words, a Gum boil is a pus-filled swelling that develops on the gums due to a bacterial infection. If it is not treated promptly, it can cause complications.
Symptoms of Gum Boils
The symptoms of a gum boil can vary depending on the severity of the infection and its cause. However, some common signs include,
- A visible lump or bump on the gums
- Swelling or redness around the affected area
- Pain or tenderness when chewing
- A bad taste in the mouth (caused by pus drainage)
- Fever or swollen lymph nodes (in severe cases)
- Bleeding gums
- Bad breath or a persistent metallic taste
In cases where the abscess breaks out, you may experience temporary pain relief, but this does not mean the infection is gone.
What Causes Gum Boils?
Several dental problems can lead to the development of gum boils, including,
- Periodontal Disease (Gum Disease): Advanced gum disease causes pockets between the teeth and gums, creating a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Tooth Infection (Periapical Abscess): An untreated cavity or trauma can allow bacteria to infect the tooth’s pulp, spreading to the surrounding tissues and gums.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Neglecting regular brushing and flossing allows plaque and bacteria to accumulate, leading to gum infection risk.
- Food Particles or Foreign Objects: Trapped food or debris between teeth and gums can lead to localized infection.
- Dental Procedures or Trauma: Any injury or irritation to the gums from braces or ill-fitting dental appliances can introduce bacteria into the gum tissue.
Risk Factors for Developing Gum Boils
Some individuals are more prone to developing gum boils due to underlying health or lifestyle factors. These include,
- Poor dental hygiene practices
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Diabetes or immune disorders
- History of periodontal disease
- Lack of routine dental checkups
- Consuming a high-sugar diet
People with weakened immune systems are especially vulnerable to infections, making it even more important to maintain good oral health.
Complications of Untreated Gum Boils
Ignoring a gum boil can have serious consequences. If the infection spreads beyond the gums, it can affect other areas, including the jaw, sinuses, or even the bloodstream, leading to a life-threatening condition known as sepsis.
Some of the complications include,
- Bone loss around teeth
- Tooth loss
- Chronic pain or swelling
- Facial cellulitis (a serious skin infection)
- Spread of infection to other parts of the body
This is why it’s crucial to seek dental care promptly if you suspect a gum boil or abscess.
How Gum Boils Are Diagnosed
A dentist can diagnose a gum boil through a combination of,
- Visual examination of the mouth and gums
- X-rays to check for underlying bone loss or tooth infection
- Pulp vitality tests to assess the health of the tooth
- Probing the gum pockets to identify infection or drainage
These diagnostic steps help pinpoint the source of the abscess and guide the appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Gum Boils
Treatment for a gum boil focuses on eliminating the infection and preventing recurrence. Depending on the severity and cause, treatment may include,
1. Drainage of the Abscess
Your dentist may make a small incision to drain the pus and relieve pressure. However, this is only temporary, and further treatment is usually necessary.
2. Root Canal Therapy
If the infection originates from within the tooth, a root canal may be performed to remove the infected pulp and seal the tooth.
3. Scaling and Root Planing
This deep-cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smooths the roots to allow healing.
4. Antibiotics
In cases of severe infection, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria and prevent the spread of the disease.
5. Tooth Extraction
If the tooth is severely damaged or beyond saving, it may need removal to stop the infection.
Home Remedies for Temporary Relief
Home remedies cannot replace professional treatment but can provide temporary relief from the discomfort caused by gum boils.
- Saltwater rinses to reduce inflammation
- Cold compresses to ease swelling
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or paracetamol
- Clove oil as a natural antibacterial agent
These remedies can soothe symptoms until you can see a dentist.
Prevention Tips for Gum Boils
Preventing gum boils is largely a matter of good oral hygiene and regular dental care. Some of the best dental care tips are,
- Brush your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss once a day to remove plaque between teeth
- Visit your dentist every six months for cleanings and checkups
- Avoid smoking and sugary foods
- Drink plenty of water to rinse away food particles and bacteria
When to See a Dentist
You should see a dentist as soon as you notice the symptoms below, as prompt treatment can prevent complications and save your teeth.
- A painful lump on your gums
- Pus discharge or a bad taste in your mouth
- Swelling that doesn’t go away
- Fever or general discomfort
Takeaway
Gum boils may seem minor at first, but they are the third most treated dental emergency. They signal serious dental infections that should not be ignored. The advancement of dentistry has helped dentists treat gumboils effectively, often quickly, and essential for preventing long-term issues.
If you suspect you have a gum boil, it’s an emergency. So, don’t wait to call Oris Dental Center to book a dental appointment to protect your oral and overall health.