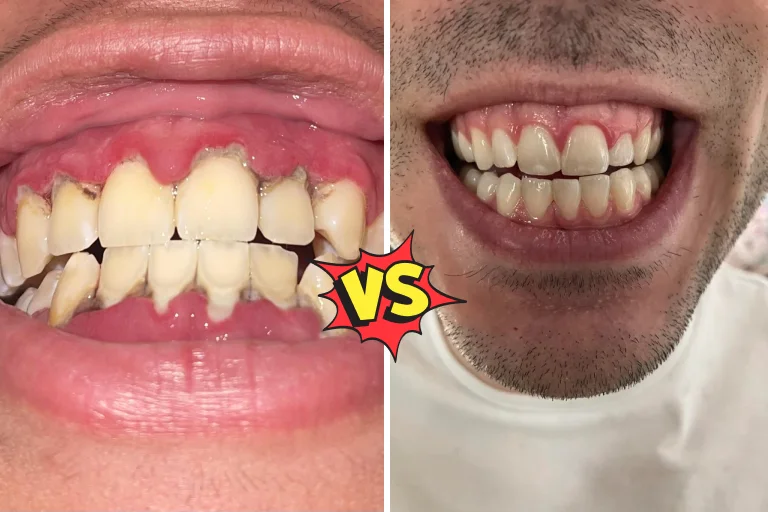
Gingivitis and periodontitis are distinct conditions that affect our gums. Both are easily treatable with good oral hygiene. So, no worries—we have explained the difference between Gingivitis and periodontitis in this blog post, along with its symptoms and treatment options.
Gingivitis vs Periodontitis
Our mouths normally contain bacteria. If bacteria build up without proper oral hygiene, it could cause gum disease. The early stages of gum disease are called Gingivitis.
If you leave Gingivitis untreated, then that could turn into periodontitis. Periodontitis is the final stage of gum disease and a very serious condition, too, as it could damage the gums and (periodontium) the bone tissue that keeps your teeth in place.
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease and also the starting stage of gum disease. So, almost everyone must have faced Gingivitis in their lifetime, and most of them don’t know they have Gingivitisit as it does not cause many symptoms. Gingivitis is easily reversible with good oral hygiene.
When gingivitis is left untreated, it can turn into a serious gum disease condition like periodontitis. So, maintaining good oral hygiene could help you get rid of the early stage of gum disease (gingivitis).
Symptoms of Gingivitis
Most often, Gingivitis does not cause any pain or major symptoms. But, we have mentioned some of the symptoms.
- Red or Swollen Gums ( puffy, inflamed, or darker in colour than usual.)
- Bleeding of gums during brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath despite good oral hygiene
How long does it take for Gingivitis to turn into periodontitis?
There is no fixed timeline for Gingivitis to turn into periodontitis. For some, this progression could take months to years. While others with poor oral hygiene or risk factors may experience a faster progression.
Risk factors that Accelerate progression
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking
- Chronic illnesses (e.g., diabetes)
- Stress Genetic predisposition
Prevention tips to stop the progression
Early intervention is the only key to stopping Gingivitis from advancing to the next stage. So, we have mentioned important tips that need to be followed. They are,
- Brushing twice daily
- Flossing regularly Using antimicrobial mouthwash
- Visiting your dentist for routine cleanings
What is periodontitis?
Periodontitis is the severe stage of gum disease that damages periodontium, which is the soft gum tissue that supports the bone of the teeth. So periodontitis is the leading cause of tooth.
Stages of Periodontitis
Periodontitis happens in three stages. The more periodontitis progresses, the more dangerous it is. There are totally three stages of periodontitis they are,
- Early Periodontitis: Slight bone loss and gum pockets up to 4 mm. The symptoms of this stage are mild symptoms like bleeding and bad breath.
- Moderate Periodontitis: Increased bone loss, gum pockets 4-6 mm. The symptoms of this stage are gum recession and possible tooth mobility.
- Advanced Periodontitis involves severe bone loss and deep gum pockets (6+ mm). The symptoms of this stage are loose teeth, pain, and possible tooth loss.
Symptoms of Periodontitis
Symptoms of Periodontitis depend on the stage of the condition. The most severe symptoms are caused by advanced periodontitis. Some of the common symptoms of periodontitis are,
- Swollen or red gums
- Bleeding gums
- Bad breath
- Receding gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pain while chewing
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Gaps forming between teeth
- Change in bite or fit of dentures
- Tooth Sensitivity
Treatment options for Periodontitis
Periodontitis is the advanced stage of gum disease, and it requires additional treatment besides maintaining good oral hygiene.
In periodontitis, early intervention and consistent follow-up with your dentist are crucial to effectively treating it. When you are affected very badly by periodontitis, the dentist may recommend the following treatment based on the stage of the periodontitis. They are,
- Scaling and Root Planning
- Antibiotic Therapy
- Surgical Treatments
- Laser Therapy
- Lifestyle Adjustments
- Maintenance Therapy
- Scaling and Root Planning: Deep cleaning procedure to remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line.
- Antibiotic Therapy: Use of topical or oral antibiotics to reduce bacterial infection.
- Surgical Treatments
Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery): Removes tartar deposits and reduces gum pockets.
Bone Grafting: Restores lost bone using grafts from your body, synthetic material, or donor tissue.
Soft Tissue Grafts: Reinforce receding gums with tissue from other areas of the mouth.
Guided Tissue Regeneration: Encourages regrowth of lost bone and gum tissue.
- Laser Therapy: A minimally invasive option to remove infected tissue and promote healing.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Quitting smoking and managing conditions like diabetes to improve treatment outcomes.
- Maintenance Therapy: Regular dental visits and professional cleanings to prevent recurrence.
Takeaway
Everyone has encountered gingivitis, which does not have any painful or disturbing symptoms. However, if you do not maintain good oral hygiene or avoid your regular dental checkup, gingivitis could turn into periodontitis. To avoid complications, maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups is very important.
Contact Oris Dental Center to avoid complicated periodontitis and control the progress of gum disease. Join Oris Dental Center to take control of your oral health.